Zhejiang Online News, January 29 (Zhejiang Online reporter Lin Jing, trainee reporter He Dongjian, and Yu Biyin) In 2021, the most stringent "plastic restriction order" in my country's history will come into effect.
Walking into major shopping malls, the plastic bags that were once available for purchase have disappeared, and the eco-friendly bags have replaced them and become a best-selling product. Many chain coffee and milk tea shops have replaced plastic straws with paper straws, but they also have disadvantages such as low strength and easy moisture absorption. For a while, "How difficult is it to drink milk tea with paper straws" has become a hot topic, and some netizens even conducted evaluations on paper straws used by different brands and shared their personal "eating" experiences.
Since its invention, plastics have brought tremendous progress to the food, clothing, housing and transportation of human beings, and have been widely used in household appliances, packaging materials, construction facilities, medical equipment and other fields. However, due to its slow degradation or even inability to degrade, the problem of "white pollution" has become an unbearable burden for the global ecological environment.
So is it possible to develop a new material that can replace plastic, break the trouble of environmental pollution, and get rid of the "yoke" of ecological destruction? What are the cutting-edge developments of biodegradable materials? A few days ago, our reporter interviewed experts and scholars in the field of materials in our province to show you the mystery.
Same as lactic acid drink
"Polylactic acid"
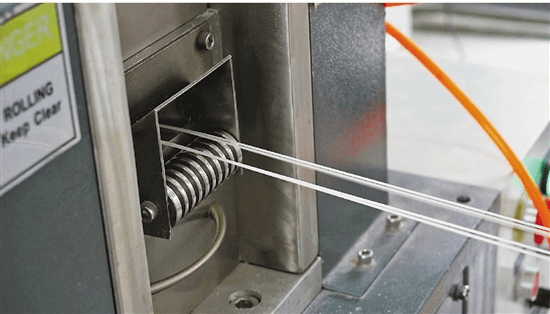
Walking into the office of Li Yongjin, a professor at the School of Materials and Chemical Engineering, Hangzhou Normal University, a large bag of straws on the table attracted reporters. "This is a completely biodegradable straw." Li Yongjin took out a thick oblique straw and squeezed it: "There is nothing wrong with puncturing the milk tea lid, and it can withstand the high temperature of 80°C, and it won't deform when drinking."
Li Yongjin told reporters that this straw is made of a material called polylactic acid, and the raw material is starch extracted from corn, potato and other biomass. After starch fermentation, lactic acid is produced, and after a certain chemical change, polylactic acid is formed by lactic acid. After use, polylactic acid can be completely degraded into water and carbon dioxide in the compost state. Therefore, polylactic acid is a degradable and recyclable material with a complete life cycle.
The ideal biodegradable material is such a polymer material, which has excellent performance and can be completely decomposed by environmental microorganisms after being discarded, and finally returns to the natural ecological cycle system. Many people may think that the degradable materials will disappear after a few weeks of burying them in the natural environment. Li Yongjin pointed out that the decomposition of degradable materials also requires time and conditions, but the degradation efficiency of degradable plastics is much higher than that of the complete degradation of general plastics for hundreds of years.
As a new type of polymer material, polylactic acid is mostly used in packaging and disposable films. It can also be used as engineering plastics in automobile and electrical appliance manufacturing. It can even be used in the medical field. At present, many manufacturers are using polylactic acid Used as a raw material for meltblown cloth to make masks.
"The clothes I wear today are made of polylactic acid fiber, which is very comfortable." Li Yongjin pointed to his collar and said, "In all areas where traditional plastic is used, it has room for its abilities."
Although the materials are good, it is difficult to promote. One of the reasons is that the heat-resistant temperature of polylactic acid itself is not very high. For example, Li Yongjin, Anhui Fengyuan Group asked him about the heat resistance of polylactic acid two years ago. They found that when the temperature reached 70°C during the blister process, the polylactic acid deformed very seriously, and the yield rate was only 30%.
The high cost is also the reason for the slow promotion of polylactic acid products. The reporter learned that the price of a ton of polyethylene, the main raw material of traditional plastic products, is about 10,000 yuan in the market. Although polylactic acid is a cheaper biodegradable material, the current cost is 30,000 yuan per ton.
At present, the dual pressures of "production costs" and "plastic restriction orders" have caused many "crooked" pseudo-degradable products to appear on the market. Li Yongjin said that about 70% of the pseudo-degradable products are traditional plastic materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene, with about 30% starch and a little photosensitizer added. After the product is discarded, under the influence of microorganisms and light, although the starch is successfully degraded, 70% of the polyethylene still remains, and it will become fragments, making it more difficult to handle.
Li Yongjin reminded that in daily life, one of the most important factors in distinguishing the authenticity of biodegradable products is the “labeling of biodegradable plastic products”. In September last year, the China National Light Industry Council formulated and issued the “Guidelines for the Classification and Labeling of Biodegradable Plastic Products”. 》, which stipulates the graphic identification of the degradable plastic "double j".
From natural plants
"Nanocellulose"
Common disposable lunch boxes, disposable tableware, disposable plastic bags... In the exhibition hall of Hangzhou Research Institute of Chemical Industry, the appearance of these degradable products looks the same as the traditional plastic products we usually use.
Yao Xianping, Dean of Hangzhou Research Institute of Chemical Industry, said: "These products are made by combining starch derivatives and nanocellulose. Unlike other products that can only be partially degraded, they can be used in the natural environment for about 6 months. All degradation, return to nature, and achieve zero pollution to the environment."
Yao Xianping introduced that the nanocellulose he studied is a fine fiber with a one-dimensional size of less than 100 nanometers, and the thickness is only one-twentieth of a human hair. Don't be confused by its "light and thin" surface. The weight of this biological material is only one-fifth of the weight of steel, but its strength is five times that. It also has a low coefficient of thermal expansion similar to that of glass fiber, and has a wide range of applications.
"Nanocellulose is very rich in raw materials. In theory, all plant cellulose can become its material." Yao Xianping said that nanocellulose is mainly made of natural biomass such as trees, waste wood, plants and waste paper. Because of its original composition, the material is recyclable and biodegradable. Therefore, nanocellulose can be combined with starch derivatives and biodegradable polymer materials to develop new fully degradable biomass materials to replace disposable plastics that are difficult to degrade and cause serious environmental pollution.
"Experiments have found that nanocellulose is naturally non-toxic and has excellent barrier properties. It can be used to prepare greaseproof paper for food and disposable paper tableware. Under its package, oxygen and water vapor cannot enter or exit. Food preservation can also shine." Yao Xianping said.
In addition, nanocellulose also has the characteristics of light weight, high strength, and good biocompatibility. With these characteristics, it can be used as high-strength and lightweight materials for vehicles such as automobiles and airplanes, as well as import materials for cosmetic nutrients and biomedical materials. A few years ago, Germany used 3D printing technology to make artificial ears for transplantation using wood nanocellulose. This artificial ear can reconstruct the auricle for children with congenital auricular deformity, so that the deformed ear can be remedied without affecting hearing.
At present, Yao Xianping’s team, with the cooperation of expert teams such as South China University of Technology and Hangzhou Institute of Mechanical and Electrical Design, has built the first domestic pilot line of 100kg/d micro/nanocellulose, which has been prepared in a green, low-cost, continuous production of nanocellulose. Major breakthroughs have been made in key technologies.
Yao Xianping told reporters that the price of zero-moisture nanocellulose in the international market is more than RMB 1 million per ton. After the pilot line is mature and the industrial line is heavily invested, the team is confident that the cost will be reduced to less than RMB 100,000.
"At this stage, the research on this new material in the world has just started, and the cost is high. It is still a question of whether the market can accept it. However, through joint technical research, we are confident to catch up with the world's advanced level." Yao Xianping is full of confidence.
Prevention everywhere
"plastic trash"
In recent years, scientists have successively discovered traces of "white rubbish" in inaccessible environments on the earth. In 2019, an explorer "coincidentally encountered" plastic waste at 10,927 meters at the bottom of the Mariana Trench. The deepest part of the earth that mankind can reach has also been invaded by "white trash".
Some scholars believe that after a few years, there may be as many plastic garbage in the ocean as there are fish in the ocean. Because plastic waste is everywhere, it is difficult for humans to find a pure land on the earth that is not polluted.
Public information shows that the world produces approximately 370 million tons of plastic each year, equivalent to the weight of 2.5 million blue whales, and more than 90% of the products are not recycled. In 2020, the "China Plastics Environmental Footprint Assessment" issued by the Natural Resources Conservation Association and the Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology pointed out that as of 2019, the cumulative output of primary form plastics in the country has exceeded 1 billion tons, and my country has become the world's largest plastic producer. And consumer countries.
Compared with "white pollution", the particle size of microplastics ranges from a few microns to a few millimeters. It is a mixture of heterogeneous plastic particles with various shapes, which is often difficult to distinguish with the naked eye. Some scholars have vividly compared it with "PM2.5". Make an analogy.
At present, most of the research on microplastic pollution is concentrated in the marine environment. It has been found that there are high concentrations of microplastics on the seabed and some deep sea areas. At the same time, there is more and more evidence that they have an impact on the health of marine species.
Feng Jie, a professor at the Institute of Polymer Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, believes that microplastics in a broad sense are not far away from us. They range from debris dropped from chemical fiber fabrics to some paste-like cosmetic additives to road tires. All of the wear and tear may contain or form microplastics. The degree of harm of microplastics depends on the specific size and the way it enters the human body. If the oral cavity accidentally ingests micron-sized microplastics, because the particles are large and cannot enter the blood through the human intestinal villi, it should be excreted. However, the oral intake of nano-scale microplastics can cause potential harm. Nano or even micron microplastics can enter the respiratory system, and may produce residues in the alveoli, causing inflammation, and ultimately causing respiratory problems.
At present, "prohibition of plastics" has become a hot social issue, but the purpose of "prohibition of plastics" is not limited to "prohibition."
In Li Yongjin's view, the purpose of "banning plastics" is to teach people how to use plastic bags. He believes: "It is said that synthetic plastic is the most important and worst invention of the 20th century, but I think it must be the best invention. If it can be used as little as possible, reused and recyclable, "white pollution" It can be avoided."
"The ban on plastics is not to let plastic products leave our lives, and to avoid the use of disposables." Chen Si, secretary general of the Zhejiang Plastics Engineering Society, said that the production capacity of degradable materials in our province is gradually increasing, and the market is occupied. The rate is getting higher and higher, and everyone is still very happy to accept biodegradable materials.
Feng Jie reminded: “At present, at least 5%-10% of plastic bags are not recycled. If traditional plastic bags are used, it will have an irreversible impact on the environment. This is the main reason why the country promotes the use of biodegradable plastics. Even if we use Biodegradable plastic bags should not be littered. They must be sorted and recycled. Once the biodegradable plastic bags enter the water system, it is difficult to say that the degradation process will not have a negative impact on aquatic animals. These are all worthy of in-depth study."